14 相対性理論 #宇宙 # 相対性理論
○宇宙は3次元の空間と時間という4次元の時空であり、空間と時間は伸びたり縮んだりする。(特殊相対性理論)
○時空を移動する光(電磁波)の速さは一定である。(特殊相対性理論)
○エネルギーと質量と光速の関係は次の式で書ける。
E=mc^2
※c^2:cの2乗
(E:エネルギー(J)、m:質量(g)、c:光の速度(m/s))
○運動する物体の質量は光速に達すると無限大になる。(特殊相対性理論)
○時空は歪んでいる。(一般相対性理論)
○宇宙は膨張している。(一般相対性理論)
○ブラックホールが存在する。(一般相対性理論)
※特殊相対性理論と一般相対性理論の2つの理論をあわせて相対性理論と呼ばれる。
※相対性理論では、ニュートン力学で記述すると誤差が大きくなる現象(光速度に近い運動や、大きな重力場における運動)を正しく記述できる。
【参 考】
1.特殊相対性理論(1905年)[電磁気力]
:電磁気学の理論。重力のない状態での慣性系を取り扱っている。
○観測者から見た「時空」は、ローレンツ変換により補正され、伸びたり縮んだりする相対的なもの。
○宇宙船の長さは前後方向に
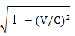
の割合で縮む。
(V:運動する速度、C:光の速度)
○運動する系では、外部の系に比べて
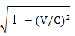
だけ時間の進み方が遅れる。
2. 一般相対性理論(1915 - 1916年)[電磁気力+重力]
:星の運動や銀河系の構造などマクロな世界の重力と時空の理論。
・質量が時空間を歪ませることによって、重力が生じることを説明した。
・ニュートンが導いた万有引力の法則を、強い重力場に対して適用できるように拡張した方程式であり、星のような物質とエネルギーの密度を右辺に代入すれば、その星の周りの時空がどういう風に曲がっているかを推定することができる。
・ニュートン力学で記述すると誤差が大きくなる現象(光速度に近い運動や、ブラックホールなどの大きな重力場における運動)を正しく記述できる。
・限られた空間に大きな質量が集中すると、ブラックホールが形成されることを予測した。
○アインシュタイン方程式(重力場の方程式)を使うと、星のような物質またはエネルギーを右辺に代入すれば、その星の周りの時空がどういう風に曲がっているかを読みとることができる。
Gμν+Λgμν=κTμν
※左辺は時空の曲率(時空の曲がり具合):銀河の全エネルギー
※右辺は宇宙に存在する物質とエネルギー(重力を生じさせるもの)の密度
⇒曲率ゼロの平坦な宇宙では、全銀河についての全エネルギーは、ゼロになる。
=平坦な宇宙では、運動が持つ正のエネルギーと重力(斥力)による負のエネルギーとの和はゼロになる。
・ Gμν:アインシュタイン・テンソル(テンソルとは歪みを表すもの。)
・Λ :宇宙定数。この項は宇宙項と呼ばれる。
アインシュタインは1917年に定常な宇宙を導くため、重力場方程式に宇宙項(:万有斥力)を加えた。
・κ :アインシュタインの重力定数。
( κ=8πG/c^4 の関係にある(π は円周率、Gは万有引力定数、c は光速))
※c^4:cの4乗(raise c to the 4 power)
・ Tμν:エネルギー・運動量テンソル。
・ 添え字μ,νは、それぞれ時空の座標を特定するもの。
○一般相対性理論は、1960年代のマイクロ波背景放射(1965)、高速回転する中性子性のパルサー(1967)、最初のブラックホール候補(1981)などの発見により確証された。
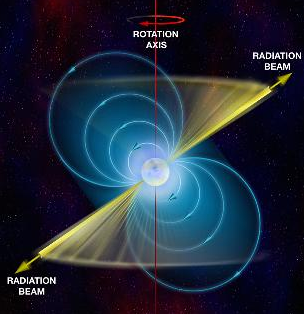
※Image of pulsar [2]
【参 照】
1. Theory of relativity - Wikipedia
2. Dave Finley “Pulsars: The Universe's Gift to Physics”at National Radio Astronomy Observatory 20120219
https://www.nrao.edu/pr/2012/aaaspulsars/
【更新履歴】
20170430 図などの追加
14 Theory of Relativity(Albert Einstein) #universe #relativity
14 Theory of Relativity(Albert Einstein) #universe #relativity
○The universe is a four-dimensional space-time consisting of three-dimensional space and time, and the space-time can shrink or elongate. (Special relativity [1])
○ The speed of light(electromagnetic wave) traveling space-time is constant. (Special relativity)
○ You can write the relationship of energy and mass and speed of light with following equation. (Special relativity)
E=mc^2
※c^2:raise c to the 4 power
(E:energy(J)、m:mass(g)、c:speed of light(m/s))
○If the mass of the object which exercises reaches speed of light, it will become infinite. (Special relativity)
○The space-time is distorted. (General relativity[2])
○ The universe is expanding. (General relativity)
○ Black hole exists. (General relativity)
※ In accordance with Special relativity and General relativity, it is called Theory of relativity.
※ According to theory of relativity, the phenomenon in which an error becomes large if Newtonian mechanics describes (movement near the speed of light and movement in a big gravitational field) , can be described correctly.
【References】
1. Special relativity(1905)[Electromagnetic force ]
:The theory which dealt with the inertia system in the state where there is no gravity.
○The universe is the 4-dimensional world of time and space. The "space-time" seen from the watcher is a relative thing which is rectified by Lorentz transformation, and is extended or is shrunk.
○The length of a spacecraft is shrunk by a cross direction at a rate of.
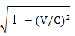
(V: Motion speed, C:Light speed)
○At the system which exercises, compared with an external system, only is delayed in time.
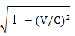
2. General relativity [Electromagnetic force + Gravity]
:Theory of gravity and space-time about the macro world such as the movement of the stars and the structure of the galaxy. (1915 - 1916)
• This theory described that gravity is generated by distortion of spacetime by mass.
・It is the extended equation of the Newton's law of universal gravitation, so that it can be applied to the strong gravitational field . By substituting the material and energy density such as a star on the right side, it is possible to estimate the curvature of the space-time around the star.
・Genera relativity can properly describe phenomenon(ex. exercise close to light-speed, or movement in a large gravitational field of such a black hole) more than Newtonian mechanics.
・Generally relativity predicts that black hole is formed where large mass is concentrated in a limited space.
○ Einstein’s equation: If you assign the mass of the material such as a star or energy in the right-hand side, it is possible to calculate the curvature of space-time around the star.
Gμν+Λgμν=κTμν
※ Left-hand side: Curvature of space-time (Geometrical quantity representing the bending of space-time):Total energy of the galaxy
※ Right-hand side: Density of matter and energy (causing a gravity) that exist in the universe
⇒In the flat universe of curvature zero, the total energy for the entire galaxy becomes zero.
=In the flat universe, the sum of the negative energy due to gravity (repulsion) and the positive energy(kinetic energy) is zero.
・Gμν:Einstein tensor(Tensor represents the distortion)
・Λgμν : The cosmological constant
・κ :Einstein's constant of gravitation
(κ=8πG/c^4 (π:pi、G:Gravitational constant、c :Speed of light))
※c^4:raise c to the 4 power
・Tμν:energy-momentum tensor
・μ, ν: Identify the coordinates of space-time.
○As astronomical phenomena were discovered, such as the 3-kelvin microwave background radiation (1965), pulsars (1967), and the first black hole candidates (1981), General relativity explained their attributes, and measurement of them further confirmed the theory.

※Image of pulsar [2]
【Referendes】
1. Theory of relativity - Wikipedia
2. Dave Finley “Pulsars: The Universe's Gift to Physics”at National Radio Astronomy Observatory 20120219
https://www.nrao.edu/pr/2012/aaaspulsars/
【Change log】
20170430 Addition of figure etc
15 量子力学 #宇宙 #力学
15 量子力学 #宇宙 #力学
15−1 量子力学とは? [1]
○語源:エネルギー、長さ、速度、時間などの物理量には、それ以上分割できない最小単位(量子)がある。
○電子(:2.8×10^−15m)程度の大きさの粒子(物質)は波動方程式(シュレディンガー方程式:偏微分方程式 1926)を解いて波動関数を得るか、ハイゼンベルクの運動方程式(行列式 1925)を解くとその状態(エネルギーの値)が分かる。
:波動関数を微分するとエネルギーや運動量の値が分かる。
※波動方程式とハイゼンベルクの運動方程式は数学的に等価。
ハイゼンベルクの運動方程式は波動方程式よりも計算が複雑になることなどから、具体的な事例の計算をおこなう場合には波動方程式を持ちいることが多く、一方で量子力学の一般論を取り扱う場合には運動方程式のほうが適したものとなっている。[2]
○波動方程式
・量子力学の基本方程式。古典力学のニュートンの運動方程式と対比される。
・物質波の状態を確率的に計算することが出来る。
・波動方程式は古典力学や数学から厳密に導けるものではない。現象を上手く説明する方程式。
※相対論は古典力学
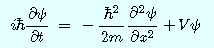
 :換算プランク定数(エイチバー)
:換算プランク定数(エイチバー)
t:時間
m:粒子の質量
Ψ(プサイ):波動関数(wave function):波動を表すために導入した複素量
X:位置
V:ポテンシャルエネルギー
○波動関数の2乗は粒子の存在確率。
・下図は物質の存在確率とエネルギー状態のグラフ。[3]
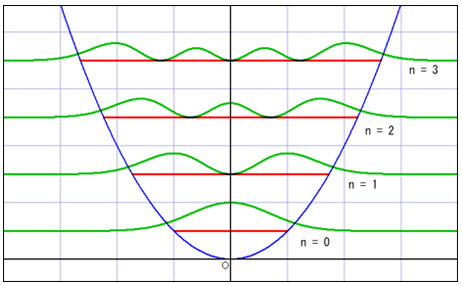
※赤色の線はエネルギーの状態(n)で、存在確率とnは飛び飛びに変化する。
※ニュートン力学の場合にはその赤線が示す幅の内側で粒子が振動するが、量子力学的な存在確率の波はその範囲を越えて広がっている。
○古典力学は量子力学の近似にすぎない。たまたま量子力学的現象が顕著でないような場合に限って古典力学を使ってもかまわない。[4]
☆宇宙は、エネルギーが数学的な規則に従うことで、全く同じ性質を持った粒子を限りなく持つ!
○量子論的な真空のゆらぎにより宇宙が誕生した。
○波動方程式が複素数を含むので波動関数は複素数の関数。
・・・宇宙は虚数によって表現される! [5]
15−2 物質波(ド・ブロイ波(de Broglie wave))の理論
○極微のレベルでは粒子と波との間に厳密な境界はない。
→波動として存在をとらえたとき、物理学ではそれを「場」と呼ぶ。たとえば光は電場と磁場の波動である。
※波としての性質が実際に観測されるのは、電子線のような極めて微視的な状況下。
※電子は波で(その大きさを求めることは不可能)、原子核における電子の軌道の長さは波長(10のマイナス10乗m)の整数倍。
=電子が原子核に落ち込まない理由
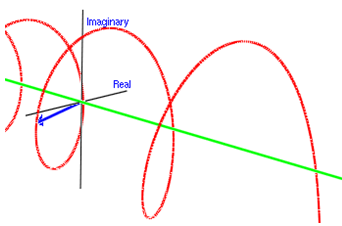
○複素数の波のイメージ [3]

※波全体が1個の粒子を表す。
※波の高さや深さは波動関数の大きさに相当する。:ド・ブロイ波=波動関数
○物質波:複素数で表される空間を動く波 [6] :方向の無いスカラー波
○一般的に物質が明らかに波としての性質を示すのは、原子を構成する電子や陽子・中性子などの素粒子の世界、1000万分の1ミリメートル(10^-10m)以下の世界。
これはナノテクノロジーなどと呼ばれるナノメートル(100万分の1ミリメートル(10^-9m))の世界の10分の1の世界。
そして原子と同じかそれより大きな世界になると、波としての性質はほとんど現れない。[2]
・しかし原子以上の世界にも、波の性質が現れてくることがある。
・その一例はヘリウムの極低温における超流動現象。「ボース・アインシュタイン凝縮」と呼ばれるもので、極低温において複数の原子の波が重なり合うことで、ボース粒子のような性質を示し、粘性がゼロになる。
※超流動とは、一定の流速以下なら液体の粘性抵抗が消失する状態。そこでは、液体が容器原子の引力に引かれて壁をよじ登り、通常の液体では通り抜けられないような狭い隙間から流れ出るなどといった、不思議な現象が見られる。[7]
※フェルミ粒子(電子、陽子、中性子)はパウリの原理に従うが、ボース粒子(光子)は従わない。
・1999年に、炭素原子60個がサッカーボール形に集まったC60分子に干渉縞を描かせることに、ウィーン大学のグループが成功した。[2]
15−3 量子力学の成果 [8]
・原子内部の運動の説明
・化学反応(共有結合)を計算で説明
・反物質、負のエネルギーの存在説明
・半導体工学の基礎理論 → 電子機器の設計
(レーザー、トランジスタ(マイクロチップ)、電子顕微鏡、MRI、発光ダイオード、USBメモリ)
・超電導、超流動の基礎理論
・量子暗号
・量子コンピュータの開発
・量子テレポーテーション
・並行宇宙論
○課題
・量子力学と一般相対性理論を合わせた理論(量子重力理論)は、いまだ完成されていない。
15−4 不確定性原理 → No.16
【参 照】
1.五十嵐靖則“量子論の世界がわかる”
https://books.google.co.jp/books?id=rJwmaVXTRRgC&pg=PA104&lpg=PA104&dq=%E8%A4%87%E7%B4%A0%E6%95%B0%E3%81%AE%E6%B3%A2%E3%81%AE%E3%82%A4%E3%83%A1%E3%83%BC%E3%82%B8&source=bl&ots=6DM1n4CVte&sig=Kjo5ljS7cub5_e8NKjOKj7CISrY&hl=ja&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiZ0978pdzOAhWGFJQKHd60AUUQ6AEIOTAM#v=onepage&q=%E8%A4%87%E7%B4%A0%E6%95%B0%E3%81%AE%E6%B3%A2%E3%81%AE%E3%82%A4%E3%83%A1%E3%83%BC%E3%82%B8&f=false
2. 佐藤勝彦”「量子論」を楽しむ本”
3.広江 克彦”EMANの量子力学”
http://eman-physics.net/quantum/contents.html
4. 量子力学 - Wikipedia
5.虚数は私たちの世界観を変えてしまった。 - とね日記
http://blog.goo.ne.jp/ktonegaw/e/ed35400df27a2bc7e597531c08d99869
6. EMAMの物理学・量子力学/調和振動子
http://eman-physics.net/quantum/oscillator.html
7. 液体ヘリウムの超流動 - 東京大学 低温センター
http://www.crc.u-tokyo.ac.jp/other/super-fluid.html
8.Quantum mechanics - Wikipedia
15 Quantum Mechanics #universe #mechanics
15 Quantum Mechanics #universe #mechanics
15−1 What is Quantum mechanics?
○Word root:Energy, length, speed, and time, those physical quantities have the smallest unit(quanta) that can not be divided any more.
○About the particles like the size of electron (: 2.8 × 10 ^ -15m), you can see the state (the value of the energy), if you get the wave function by solving the wave equation (Schrodinger equation: partial differential equation 1926) , or if you solve Heisenberg`s equation (the determinant 1925) .
:By differentiating the wave function, we know the values of energy and momentum.
※The wave equation and Heisenberg`s equation is mathematically equivalent.
Since Heisenberg`s equation is more complicated than the wave equation, computation of concrete cases often uses wave equations. On the other hand, when dealing with the general theory of quantum mechanics Heisenberg`s equation is more suitable.
○The Wave equation
• The Wave equation is a Fundamental equation of quantum mechanics. It is contrasted with Newton's equation of motion of classical mechanics.
・We can calculate the state of the matter wave stochastically by the equation.
・The Wave equation cannot be obtained strictly by using classical mechanics or mathematics. It is the equation that successfully describes the physical phenomena.
※Relativity is classical mechanics.
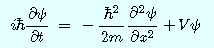
 : reduced Planck constant
: reduced Planck constant
t:time
m: mass of particle
Ψ(Psi):wave function: Complex quantity, which was introduced to represent the wave
X:position
V: potential energy
○The squared modulus of the wave function is a real number interpreted as the probability density of measuring a particle's being detected at a given place.
・The figure below shows the graph of the probability density and the energy state of matter. [1]

※The red line is the energy state(n). The probability density and n is changed at intervals.
☆The universe had particles that have exactly the same properties without limit, at energy following the mathematical rules!
○The universe was born from a quantum fluctuation.
○Wave function is a function of the complex because the wave equation contains complex number. [2]
・・・The universe is represented by imaginary!
15−2 Material Wave(de Broglie wave)
○On a submicroscopic level, there is no boundary strict between particles and wave.
→When existence is regarded as a wave motion, in physics, it is called a "place." For example, light is wave motion of an electric field and magnetic field.
※ It is under a very microscopic situation like an electron beam that the character as a wave is actually observed.
※ It is impossible to determine the size of the electron.
※ And the length of orbit around the nucleus is an integer multiple of the wavelength (10 minus 10 square m).
=Why the electrons are not getting stuck in the nucleus.
○The image of the wave of complex number [1]

※Whole wave represents one of the particles.
※Height and depth of the wave corresponds to the size of the wave function.
:de Broglie wave=the wave function
○Material Wave:A wave that moves the space represented by the complex number. [3]:without direction(Scalar wave)

○In general, the substance obviously shows the property of waves is the world of elemental particles such as electrons composing atoms, protons and neutrons, the world of less than 10 millionths of a millimeter (10 ^ -10 m).
This is one tenth of a world of nanometer (one millionth of a millimeter (10 ^ - 9 m)) called nanotechnology etc.
And when becoming a world equal to or larger than an atom, the property as a wave hardly appears.
• However, in the world beyond atoms, the nature of waves may appear.
・One example is the superfluid phenomenon of helium at cryogenic temperature. This is called "Bose-Einstein condensation", and the waves of a plurality of atoms overlap each other at cryogenic temperature, thereby exhibiting properties like Bose particles, and the viscosity becomes zero.
※Superfluid refers to a state in which the viscous resistance of a liquid disappears at a constant flow rate or less. There are strange phenomena, such as the liquid climbing the wall by the attraction of the container atom and flowing out from the narrow gap which can not be passed by ordinary liquid.
※Fermi particles (electrons, protons, neutrons) follow Pauli exclusion principle , but Bose particles (photons) do not follow.
・In 1999, the group of Vienna University succeeded to let C60 molecules with 60 carbon atoms gather in the form of soccer balls to draw interference fringes.
15−3 Applications [4]
・Description of the behaviors of the subatomic particles
・Computational chemistry
・The presence description of antimatter and negative energy
・Basic theory of semiconductor engineering → Electronic devices design
(the laser, the transistor (and thus the microchip), the electron microscope, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) , the light emitting diode, USB drives)
・Basic theory of superconductivity and superfluidity
・Quantum cryptography
・Quantum computing
・Quantum teleportation
・Parallel universes
○Unsolved problem
・Quantum gravity theory is incomplete.
15−4 Uncertainty Principle → No.16
【References】
1. 広江克彦”EMANの量子力学” Katsuhiko Hioe” EMAN’s Quantum mechanics”(Japanese)
http://eman-physics.net/quantum/contents.html
2.Lecture 3: The Wave Function - MIT OpenCourseWare
http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/physics/8-04-quantum-physics-i-spring-2013/lecture-notes/MIT8_04S13_Lec03.pdf
3. EMAMの物理学・量子力学/調和振動子 EMAN’s Physics ・Quantum mechanics/ harmonic oscillator (Japanese)
http://eman-physics.net/quantum/oscillator.html
4. Quantum mechanics - Wikipedia
【Change log】
20170929 Addition about Material Wave, the wave equation and Heisenberg`s equation
16 不確定性原理 #宇宙 #不確定性
16 不確定性原理 #宇宙 #不確定性
16−1 1927年 ハイゼンベルク
量子のレベルでは、ある粒子(たとえば電子)について、その位置と運動量は確率でしか答えられないという原理。
○位置の標準偏差σxと運動量の標準偏差σpを結び付ける不等式
σxσp≧h
:どんなに測定の精度を高めても、位置と運動量の標準偏差の積はhよりも大きくなる。
:片方を確定しようとすると片方が不確定になる。
・x:位置、p:運動量
・h:プランク定数(6.626×10^-34ジュール・秒)
:粒子はある範囲の中に広がって存在している。
○エネルギーと時間の場合
σEσt≧h
:少しだけエネルギー保存則を破って、エネルギーを借りても良い。
※ただしたくさん借りるほど早く返さなければならない。
・E:借りるエネルギーの量、t:借りる時間
⇒エネルギーは物質化する。⇒粒子・反粒子が現れては消えている。[3]
=量子ゆらぎ
⇒真空でも、粒子・反粒子が現れては消えている。:真空のゆらぎ
⇒真空はただのゼロではなく、正と負のエネルギーがせめぎあい全体としてプラス・マイナスでゼロになっている。
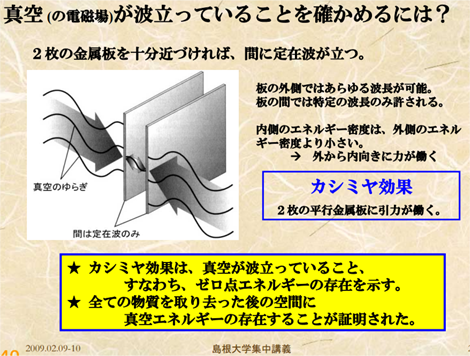
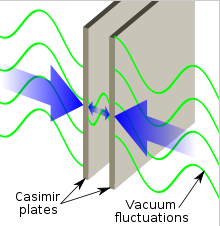
・真空のゆらぎは極微において計測可能な力(カシミール効果)を引き起こす。
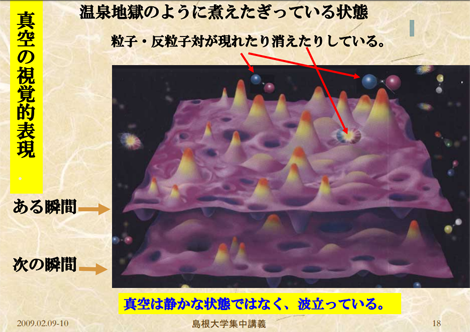
図:真空のゆらぎ [3]
16−2 カシミール効果(Casimir effect)
○非常に小さい距離を隔てて設置された二枚の平面金属板が真空中で互いに引き合う現象を、静的カシミール効果という。
○静的カシミール効果の引力作用は、二枚の金属板の間には真空エネルギーの一部の波しか入り込むことができないことから、真空エネルギーの密度が外側よりも減少することにより生じる。
○また、二枚の金属板を振動させると光子やエネルギーが生じる。これを動的カシミール効果という。 [4]
○動的カシミール効果では、大量のエネルギーを要するが、理論的には電子や陽子などの他の粒子も、真空から生成することが可能。また、量子コンピュータの開発などに役立つ可能性がある。[5]
16−3 真空の相転移/インフレーション宇宙/トンネル効果 [6]
○真空はよりエネルギーの低い状態の真空へと移行(相転移)する。
○現在の宇宙論では、宇宙誕生の10^-36秒から10^-34秒後の間に、インフレーションと呼ばれる指数関数的な急激な膨張(原子(1e-10m)よりはるかに小さい実宇宙(1e-27m)⇒3ミリ程度(1e-3m))があったとされている。
○このインフレーションの原動力となったのは、真空の相転移の際に解放されたエネルギーだとされている。
○初期のインフレーション理論では、偽の真空と真の真空の間に明確なポテンシャルの障壁があり、それをトンネル効果によって乗り越えることで真空の相転移が発生すると考えられていたが、新しいインフレーション理論(ゆっくり転がるインフレーション)では、明確なポテンシャルの障壁はなく、偽の真空から真の真空へと至る緩やかなポテンシャルの坂があるとされている。
※トンネル効果:エネルギーの壁を、それより低いエネルギーを持った粒子が通り抜けてしまう現象。古典的に考えればトンネルを掘らない限りは不可能に思えるが、量子論では不確定性原理により、あたかもトンネルを掘ったかのように障壁を乗り越えてしまうことがある。半導体はこの原理を利用してつくられている。[7]
※α崩壊とトンネル効果
シュレジンガー方程式を解いてアルファ粒子の位置を計算すると、α粒子が原子の外側にも存在できる:原子核の縁のエネルギーの壁を、トンネルを掘るようにして通り抜けることができる。[8]
※核融合もトンネル効果のおかげ。トンネル効果がなければ、陽子同士は衝突できない。太陽が輝くこともない。[9]
【参考】
1. 不確定性原理 - Wikipwdia
2. ハイゼンベルクの不確定性原理 - nifty
http://homepage2.nifty.com/einstein/contents/relativity/contents/relativity3055.html
3. 島根大学集中講義 真空の性質2009
http://osksn2.hep.sci.osaka-u.ac.jp/~naga/kogi/shimane-class09/shimanelec2_vac.pdf
4. カシミール効果 - Wikipedia
5.SJN news” チャルマース工科大、真空から光子を生成。「動的カシミール効果」を実験で確認”(2011)
http://sustainablejapan.net/?p=980
6. 偽の真空 – Wikipwdia
7. トンネル効果 - Wikipwdia
8. 佐藤勝彦”「量子論」を楽しむ本”
9.前野昌弘 “量子力学入門" 20060216 (p.107)
http://www.phys.u-ryukyu.ac.jp/~maeno/qm/qm.pdf
【更新履歴】
20170930 トンネル効果について追記
16 Uncertainty Principle #universe #uncertainty
16 Uncertainty Principle #universe #uncertainty
16−1 1927 Werner Heisenberg
Introduced first in 1927, by the German physicist Werner Heisenberg, it states that the more precisely the position of some particle is determined, the less precisely its momentum can be known, and vice versa.
You can answer only according to probability on the level of quantum.
○The formal inequality relating the standard deviation of position σx and the standard deviation of momentum σp
σxσp≧h
:No matter how improve the accuracy of the measurement, the product of the standard deviation of the position and momentum is greater than h.
:One is uncertain when you try to confirm the other.
・x:position、p:momentum
・h:Planck constant(6.626×10^-34 J・s)
: Particles are spread out within a certain range and exist on the level of quantum.
○In the case of energy and time
σEσt≧h
:Beating only a little law of conservation of energy, it may be borrowed energy.
※However it must return as fast as borrow a lot.
・E:energy、t: time
⇒Energy is possible to materialize.⇒Pairs of matter and anti-matter particles are constantly being created and annihilated.
=Quantum fluctuations
⇒Also in vacuum, pairs of matter and anti-matter particles are constantly being created and annihilated.: Vacuum fluctuations
⇒The vacuum has a vastly complex structure.
・Vacuum fluctuations causes a measurable force (Casimir effect) in infinitesimal.

※Vacuum fluctuations [3]
16−2 Casimir effect
○The typical example is of the two uncharged conductive plates in a vacuum, placed a few nanometers apart. The Casimir effect produces the negative pressure. It is due to quantum vacuum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field.
○As the two mirrors move closer to each other, the longer waves will no longer fit--the result being that the total amount of energy in the vacuum between the plates will be a bit less than the amount elsewhere in the vacuum. Thus, the mirrors will attract each other, just as two objects held together by a stretched spring will move together as the energy stored in the spring decreases. [4]
○The dynamical Casimir effect is the production of particles and energy from an accelerated moving mirror. [5] Further, there may help development of quantum computers.
16−3 Phase Transitions of Vacuum /Inflation Cosmology/Quantum Tunneling
○Vacuum is to shift to more of the state of low energy:phase transition.
○In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation, or just inflation is a theory of exponential expansion of space in the early universe. The inflationary epoch lasted from 10 minus 36 square seconds until after 10 minus 34 square seconds.
(The size of the universe (10^-27m) is much smaller than atom (10^-10m).
⇒3 millimeters (10^-3m))
○The driving force behind this inflation has been said that the energy that was released during the phase transition of the vacuum.
○In early inflationary models, the phase transition of the vacuum was considered that it is generated by the Quantum tunnelling or tunnel effect. However, in a model named new inflation or slow-roll inflation, instead of tunneling out of a false vacuum state, inflation is considered that occurred by rolling down a potential energy hill.
※Quantum tunnelling or tunnel effect to the quantum mechanical phenomenon where a particle tunnels through a barrier that it classicallycould not surmount. In the quantum theory it is explained by the uncertainty principle.
It has important applications to modern devices such as the tunnel diode, quantum computing, and the scanning tunnelling microscope. [3]
※α decay and tunnel effect
Calculating the position of alpha particles by solving the Schlesinger equation, the α particles can also be present outside the atoms. Actually in α decay, α particles can go through the walls of energy at the edge of nuclei, digging tunnels.
※Nuclear fusion is also thanks to the tunnel effect. Without the tunnel effect protons can not collide with each other. And the sun can not shine. [6]
【Refereces】
1.Wikipedia: Uncertainty principle
2. ハイゼンベルクの不確定性原理 - nifty Uncertainty principle- nifty
http://homepage2.nifty.com/einstein/contents/relativity/contents/relativity3055.html
3.RevoScience”Young researcher proposes new explaination for unsolved problems in physics…”
http://revoscience.com/en/young-researcher-proposes-new-explaination-for-unsolved-problems-in-physics-and-revolutionizes-the-theory-of-quantum-fluctuations/
4. “What is the Casimir effect?”SCUENTIFIC AMERICAN 1998
http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/what-is-the-casimir-effec/
5. Wikipedia:Casimir effect
6. Masahiro Maeno “Introduction to Quantum mechanics(Japanese) " 20060216 (p.107)
http://www.phys.u-ryukyu.ac.jp/~maeno/qm/qm.pdf
【Change log】
20170930 Addition about tunnel effect