11 星の誕生と寿命 #宇宙 #寿命
11 星の誕生と寿命 #宇宙 #寿命
11−1 星の誕生
宇宙では
カオスの中から星が生まれる。
エントロピーを増大させつつ星や知性が生まれている。
※エントロピー:無秩序の程度
※エントロピー増大の法則:宇宙では無秩序が増大するという法則。
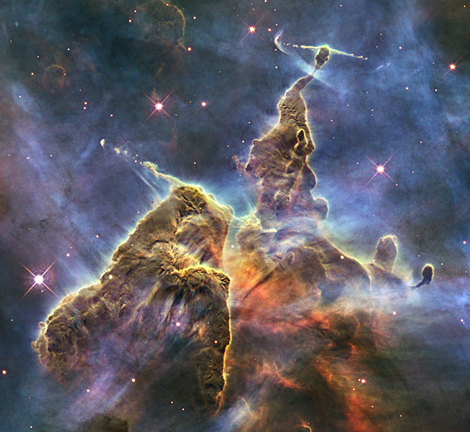

※カリーナ星雲(7,500光年)
(c)NASA,ESA,and M.Livio and the Hubble 20th Anniversary Team(STScI)
11−2 星の寿命 【宇宙とは】宇宙との対話 [1]
○質量の大きな星ほど早く燃え尽きる。
(星の寿命は質量の 2 乗から 3 乗に反比例している。)
○太陽の寿命は約100 億年。太陽の10 倍の星の寿命はおよそ1/100 から 1/1000 の 1 億年から 1000 万年。
○太陽の推測年齢は46億年であることから、余命は約50億年。
【Refereces】
1. 星には寿命があるのでしょうか? 理科年表オフィシャルサイト
https://www.rikanenpyo.jp/FAQ/tenmon/faq_ten_004.html
【履 歴】
20180913 図の整理
11 The Birth and Life of Stars #universe #life
11 The Birth and Life of Stars #universe #life
11−1 The Birth of Stars
In the universe,
Stars are born from chaos.
Stars and intelligence are being born while increasing the entropy.
※ entropy: the degree of disorder
※ law of entropy increase: the laws of increasing of disorder in the universe

※The Carina Nebula (7,500 ly)
(c)NASA,ESA,and M.Livio and the Hubble 20th Anniversary Team(STScI)
11−2 Life of Stars
○Big star burns out faster than small one.
(Since stars have a limited supply of hydrogen in their cores, they have a limited lifetime as main sequence stars. This lifetime is proportional to f M / L, where f is the fraction of the total mass of the star, M, available for nuclear burning in the core and L is the average luminosity of the star during its main sequence lifetime. Because of the strong dependence of luminosity on mass, stellar lifetimes depend sensitively on mass.)
・The Life and Death of Stars NASA
○The lifetime of the sun is about 100 million years. The life of stars of 10 times weight of the sun is from 1 / 1000 to 1 / 100.
○The Sun formed about 4.6 billion years ago. It will exit the main sequence in approximately 5 billion years and start to turn into a red giant. [2]
・Sun −Wikipedia:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sun#Life_phases
【Change log】
20180913 Organize diagram
12 宇宙の歴史[1] #宇宙 #歴史
12 宇宙の歴史[1] #宇宙 #歴史
0 量子的揺らぎ [2]
10^-36〜10^-34秒後 インフレーション(10^-27→10^-3m、10^28→10^25K)[3]
〜10^-32秒後 ビッグバン(10^-1m=10cm)[4]
10^-9秒後 質量の誕生(10^13K)[5]
1秒後 宇宙が太陽系の大きさになる。(10^13m、10^10K)
100秒後 水素とヘリウムの誕生(10^9K)
30万年後 宇宙の晴れ上がり:マイクロ波背景放射で観察される
(10^24m=8,200万光年、3000K、宇宙の拡大速度:光速の60倍)
5億年後 恒星の誕生
6億年後 銀河の誕生
50億年後〜 第2次インフレーション [3]
90億年後 太陽系の誕生
138億年後 現在
(10^27m=900億光年、2.7K、宇宙の拡大速度:光速の3.5倍)
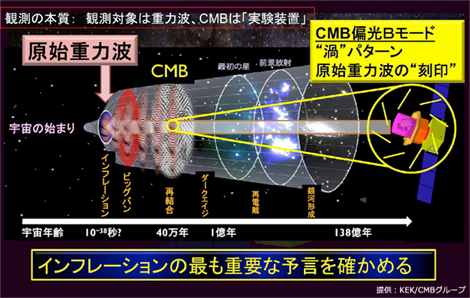
※ 宇宙の歴史 [6]
【参 照】
1. Wikipedia:宇宙の年表
2. No.21−1 宇宙の誕生:量子的ゆらぎ
3. No.21−2 インフレーション理論
4. No.21−4 ビッグバン理論
5. No.23 ヒッグス場/ヒッグス粒子
6. 三菱電機”宇宙創生時の急膨脹「インフレーション」の証拠写真を撮る日”
12 History of the Universe[1] #universe #history
12 History of the Universe[1] #universe #history
0 The quantum fluctuation [2]
After 10^-36〜10^-34 second Inflation(10^-27→10^-3m、10^28→10^25K)[3]
〜10^-32 second Big Bang(10^-1m=10cm)[4]
After 10^-9 second The birth of mass(10^13K)[5]
After 1 second The Universe had become the size of the solar system.
(10^13m、10^10K)
After 100 seconds The birth of hydrogen and helium10^9K)
After 300,000 years Transparent to radiation:The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the oldest light in the universe.
(0^24m=82 million ly、3000K、Expansion rate of the universe: 60 times the speed of light)
After 0.5 billion years The birth of stars
After 0.6 billion years The birth of galaxies
5 billion years 〜 Second Inflation [3]
After 9 billion years The birth of Solar system
After 13.8 billion years Current
(10^27m=90 billion ly、2.7K、Expansion rate of the universe: 3.5 times the speed of light)
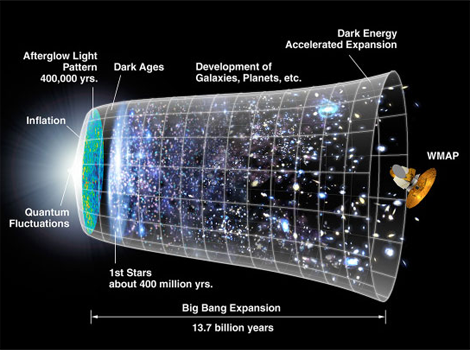
※ Chronology of the universe [1]
【References】
1. Chronology of the universe− Wikipedia
2. No.21−1 The Birth of the universe:Quantum fluctuation
3. No.21−2 Inflation cosmology
4. No.21−4 The Big Bang model
5. No.23 Higgs field and Higgs Boson
13 Newtonian Mechanics #universe #Mechanics
13 Newtonian Mechanics #universe #Mechanics
・Three laws of Newtonian mechanics
1) Law of inertia・・・As for an object, unless power acts -- stillness -- linear uniform motion is carried out.
2) Equation of motion・・・At a mass point the acceleration(a) is proportional to the power(F) of acting then, and is in inverse proportion to the mass(m).
F=ma
3) Action-reaction law
・Law of universal gravitation
○Newtonian mechanics can be used when treating movement of sufficiently later than the velocity of light in a macroscopic scale(0.1 mm or more). For example, in the space navigation in an artificial satellite or planetary exploration, it is calculable in sufficient accuracy using Newtonian mechanics in many cases.

【Change log】
20170501 Addition of a photo
