28 Loop Quantum Gravity(LQG)
28 Loop Quantum Gravity(LQG) 【What is the Universe?】Dialogue with the Universe
[Electromagnetic force + Weak interaction+Strong interaction + Gravity]
・LQG is an attempt to merge quantum mechanics and general relativity. [1]
・Quantum gravity (QG) is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe the force of gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics.
28−1 Overview [1]
○In the loop models, the basic structure of space-time turns out to be discrete. In such discrete space-times, there are smallest values for volumes and areas that are not divisible any farther.
○The granular structure of space-time gets rid of the infinities that plague quantum field theory.
○Elementary particles for each type, the rotational speed takes the value of the discrete, as the basic number of Planck constant. For example, an electron rotates at half the speed of Planck constant.
<Decide the direction of the space from the spin direction of the particle>
・In the 1950s, by utilizing this principles of the spin, "the Spin network" theory which defines the direction of each point in space from the direction of the electron spin published by Penrose.
・As a specific method, the theory represents a material at a point, and represents the direction at a line, and make a constant volume by planes perpendicular to the line.
・The predicted size of this structure is the Planck length, which is approximately 10−35 meters.
・Space can be viewed as an extremely fine fabric or network "woven" of finite loops. These networks of loops are called spin networks.
・This change in spin network indicates the presence of gravity and elementary particles.
・The granular structure of space-time that is implied by spin networks also gets rid of the infinities that plague quantum field theory.
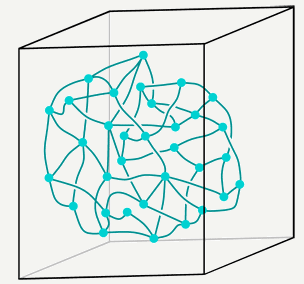
※Spin networks [2]
<Loop quantum gravity theory creates space, gravity and substance at a time>
・The evolution of a spin network over time is called a spin foam.
・Spin form changes discretely.
• The time difference is 1 Planck seconds of the change (10-43 seconds), and the time that people feel is what this very short time is stacked.
・The main output of LQG is a physical picture of space where space is granular. It has the same nature as the granularity of the photons in the quantum theory of electromagnetism and the discrete levels of the energy of the atoms.
28−2 Difference from super string theory
1)In string theory( a quantum theories of gravity) one generally starts with quantized excitations on top of a classically fixed background. LQG is thus described as background dependent. In contrast, LQG, like general relativity, is manifestly background independent. [1]
2)Super string theory requires that space-time have 10 dimensions; LQG is formulated in 4 dimensions. [3]
3)String theory also implies the existence of supersymmetry, in which all known particles have yet-undiscovered partners. Supersymmetry isn’t a feature of LQG. [1] [3]
4)In loop quantum gravity, there is no big bang singularity; instead, the universe´s history can be traced infinitely far into the past, step by step. [2]
※An inflationary expansion might have been driven by quantum-gravitational effects. [4]
○ Task
・Quantum gravity effects are notoriously difficult to measure because the Planck length is so incredibly small. However recently physicists have started to consider the possibility of measuring quantum gravity effects. [5]
・The Universe can be used as a laboratory to test quantum gravity effects. First, there are accelerators in distant galaxies that produced gamma burst, 10 billion years ago, particles with energies much higher than we can produce in even the largest man-made accelerators, 10 million times higher. Secondly, due to the long times and vast distances involved, effects such as the difference in speeds of these particles (speed of light is energy dependent according to LQG) can be detected over these long distances and times. [4] [6]
・In 2015, the Advanced LIGO team announced that they had detected gravitational waves from a pair of black holes merging. [7] [8]
【References】
1. Loop quantum gravity - Wikipedia
2. Loop quantum gravity — Einstein Online
http://www.einstein-online.info/elementary/quantum/loops
3.String Theory Meets Loop Quantum Gravity | Quanta Magazine
https://www.quantamagazine.org/20160112-string-theory-meets-loop-quantum-gravity/
4. Carol Rovelli“Loop quantum gravity”
http://igpg.gravity.psu.edu/people/Ashtekar/articles/rovelli03.pdf
5.Quantum gravity (QG) - Wikipedia
6.Duality of Spacetime and Matter - NCF.ca
http://web.ncf.ca/fm120/Physics/LQG/Duality_Spacetime_and_Matter,_draft_2004-01-07.htm
7.Gravitational wave - Wikipedia
8.No.30 Gravitational Wave
【Change log】
20170421 Split into 3 items
28 ループ量子重力理論 【宇宙とは】宇宙との対話
[電磁気力+弱い力+強い力+重力]
・一般相対論と量子論を統合しようとする理論
・量子力学の原理に基づいて重力の力を説明しようとする量子重力理論の一つ。
28−1 概要 [1][2]
○時空(時間と空間)にはそれ以上の分割不可能な最小単位が存在する。
○この理論で時空は、結晶格子のように離散的な値をとるものと考えられている。このため、時空を連続的なものととらえたときに起きる短距離極限の発散が生じないという利点がある。
○粒子は種類ごとに、プランク定数という数を基本として、その回転数は飛び飛びの値を取っている。例えば電子は、プランク定数の1/2の速度で回転している。
<粒子のスピンの方向から、空間の方向を決める。>
・1950年代に、このスピンの原理を利用して、電子のスピンの方向から、空間の各点の方向を定義する「スピンネットワーク」理論が、ペンローズによって発表された。
・具体的な方法としては物質を点で表し、方向性を線で表して、その線に垂直な面で一定の体積を作る。
・そのサイズはプランク長(10^-35m)。
・これを空間の最小単位(量子)として、方向を表す線をなぞって一周する(ループを描く)と空間の方向の変化が分かる。
・この理論で時空は、点と線を使ってグラフで表される。このグラフはスピンネットワークと呼ばれる。
・このスピンネットワークの変化が重力や素粒子の存在を示していると考える。

※スピンネットワーク[3]
<空間、重力、物質を一度に生み出し、表現できるのがループ量子重力理論の特徴>
・スピンネットワークに時間を加えたものをスピンフォームと呼ぶ。
・スピンフォームは時計の秒針が動くように離散的に変化する。
・変化前と変化後の時間の差は1プランク秒(10^-43秒)で、これが積もり積もって人が感じる時間となる。
・このようにループ量子重力理論では、時空は原子における電子配置のように離散的な値をとるものと考えられている。
28−2 超弦理論との相違
1)ループ量子重力理論と同じく量子重力理論の候補である超弦理論は、時空は背景場として最初からそこに存在するものとして定義しているが、ループ量子重力理論は、一般相対論と同様に理論自身が時空そのものを決定している。(背景独立性)
2)超弦理論では時空が10次元だが、ループ量子重力理論は、4次元。[4]
3)超弦理論ではすべての粒子が超対称性パートナーを有することになるが、ループ量子重力理論は超対称性を用いずに展開できる。[4]
4)ループ量子重力理論では、ビッグバンのような特異点は存在せず、宇宙の歴史は無限に遡ることができる。[3]
※インフレーションは量子重力効果によって引き起こされた。[5]・・・?
28−3 課題・今後の展開
・重力は自然界に存在する四つの力(基本相互作用)の中で最も弱く量子化された重力の観測が困難.。
・空間の構造が離散的だとすると,そこを伝わる光のスピードは波長によってわずかに異なる。はるか遠くの宇宙で発生したガンマ線バーストの光が,波長によってわずかな時間差をもって地球に届くことが検出されれば,理論を実証できる。[5] [6]
・2015年 カリフォルニア工科大とマサチューセッツ工科大などの共同研究チームが重力波を初検出。 [7]
【参考】
1. ループ量子重力理論 - Wikipedia
2. 教えて!goo
http://oshiete.goo.ne.jp/qa/1474170.html
3.Loop quantum gravity — Einstein Online
http://www.einstein-online.info/elementary/quantum/loops
4.リー・スモーリン ”時空の原子を追うループ量子重力理論”
http://www.nikkei-science.com/page/magazine/0404/loop.html
5.Carol Rovelli“Loop quantum gravity”
http://igpg.gravity.psu.edu/people/Ashtekar/articles/rovelli03.pdf
6.産経新聞 20160212
http://headlines.yahoo.co.jp/hl?a=20160212-00000502-san-sctch
7.No. 30 重力波
【更新履歴】
20170421 3項目に分割